1. Introduction#
1.1. API’s of imbalanced-learn samplers#
The available samplers follow the
scikit-learn API
using the base estimator
and incorporating a sampling functionality via the sample method:
- Estimator:
The base object, implements a
fitmethod to learn from data:estimator = obj.fit(data, targets)
- Resampler:
To resample a data sets, each sampler implements a
fit_resamplemethod:data_resampled, targets_resampled = obj.fit_resample(data, targets)
Imbalanced-learn samplers accept the same inputs as scikit-learn estimators:
data, 2-dimensional array-like structures, such as:Python’s list of lists
list,Numpy arrays
numpy.ndarray,Panda dataframes
pandas.DataFrame,Scipy sparse matrices
scipy.sparse.csr_matrixorscipy.sparse.csc_matrix;
targets, 1-dimensional array-like structures, such as:Numpy arrays
numpy.ndarray,Pandas series
pandas.Series.
The output will be of the following type:
data_resampled, 2-dimensional aray-like structures, such as:Numpy arrays
numpy.ndarray,Pandas dataframes
pandas.DataFrame,Scipy sparse matrices
scipy.sparse.csr_matrixorscipy.sparse.csc_matrix;
targets_resampled, 1-dimensional array-like structures, such as:Numpy arrays
numpy.ndarray,Pandas series
pandas.Series.
1.2. Problem statement regarding imbalanced data sets#
The learning and prediction phrases of machine learning algorithms can be impacted by the issue of imbalanced datasets. This imbalance refers to the difference in the number of samples across different classes. We demonstrate the effect of training a Logistic Regression classifier with varying levels of class balancing by adjusting their weights.
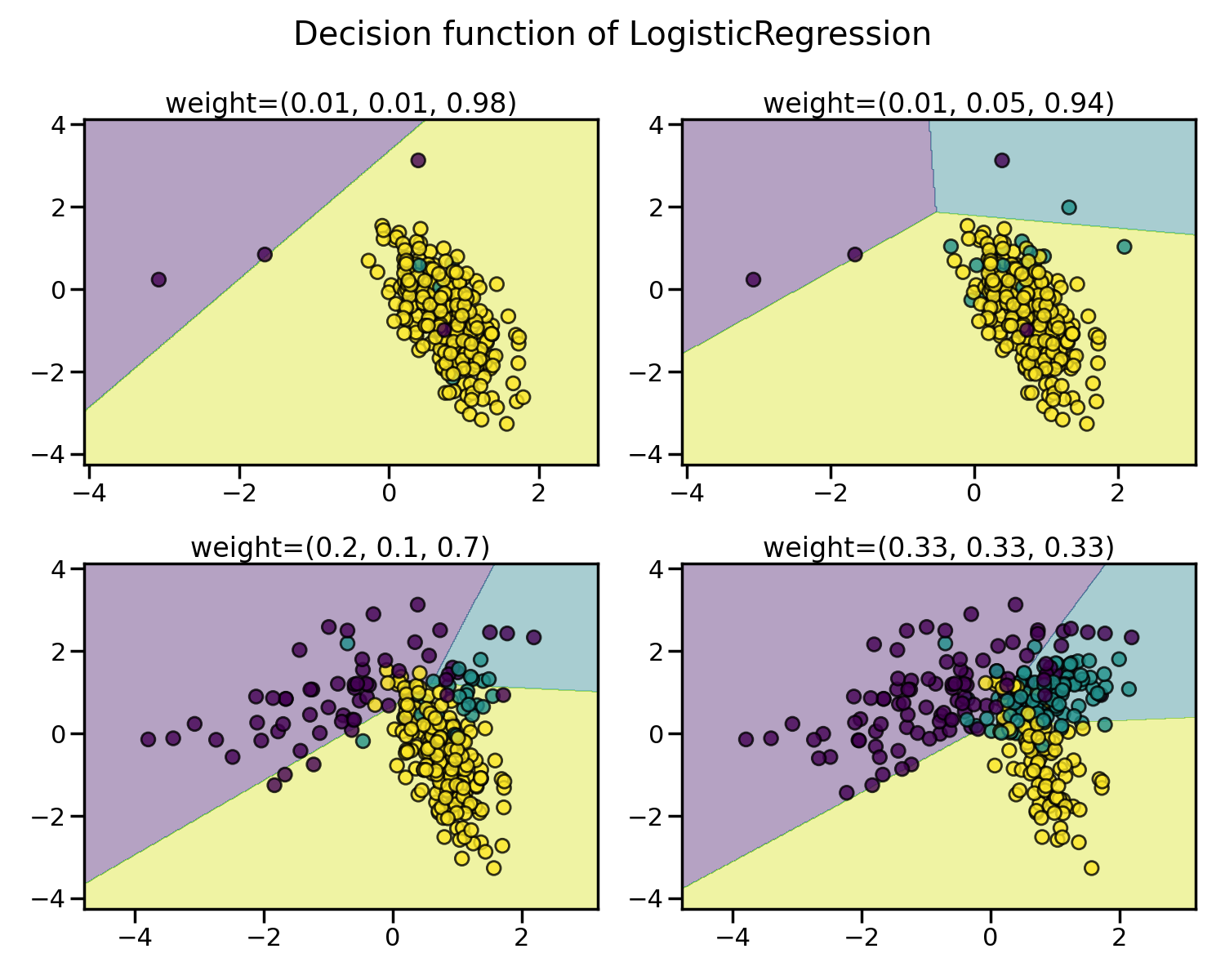
As expected, the decision function of the Logistic Regression classifier varies significantly depending on how imbalanced the data is. With a greater imbalance ratio, the decision function tends to favour the class with the larger number of samples, usually referred to as the majority class.

